FHIR Validation Guide
Overview
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server validation module (fhir-validation) provides Java APIs for validating FHIR resources using constraints specified in their corresponding structure definitions.
The validation module is available from our Maven artifact repository and is also packaged together with its dependencies and all of our pre-packaged implementation guides in the fhir-validation-distribution.zip artifact which may be downloaded from https://github.com/LinuxForHealth/FHIR/releases.
How it works
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server validation module evaluates constraints from both the core specification and from structure definitions that are available at runtime. For example, in the Patient resource, we have the following constraint:
@Constraint(id = "pat-1",level = "Rule",location = "Patient.contact",description = "SHALL at least contain a contact's details or a reference to an organization",expression = "name.exists() or telecom.exists() or address.exists() or organization.exists()")
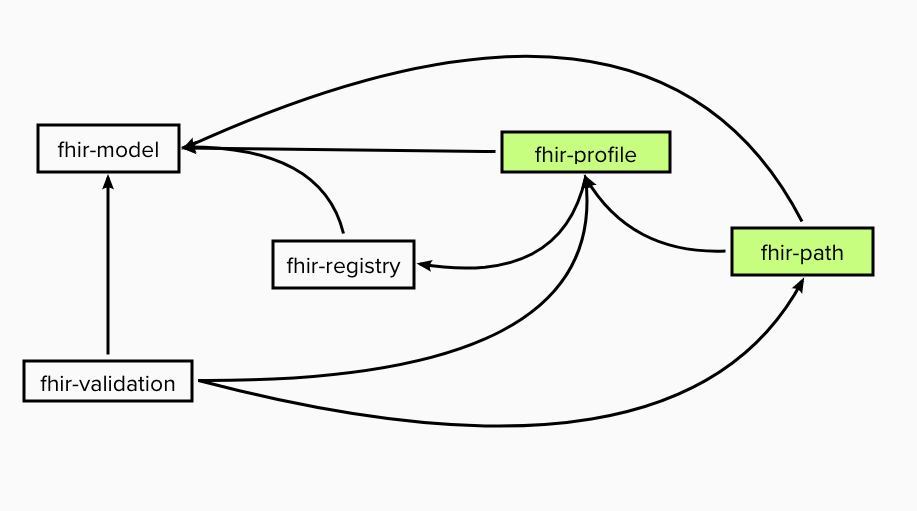
The validation component picks up the Java annotation, pulls out the FHIRPath expression and passes it on to the LinuxForHealth FHIR Server FHIRPath component (fhir-path) for evaluation. If the invariant evaluates to false then the FHIR validator will generate an OperationOutcome.Issue with the severity set relative to the “level” of the constraint (i.e. “Rule” or “Warning”);
Profile Support
The validation component will also validate a resource against profiles that it asserts conformance to in the Resource.meta.profile element assuming those profiles are available to the LinuxForHealth FHIR Server via the FHIR registry component (fhir-registry) at runtime.
Given a FHIR profile (structure definition) that contains a Snapshot as input, the LinuxForHealth FHIR Server Profile component (fhir-profile) generates FHIRPath expressions for a number of different types of constraints. The current scope of constraint generation is:
- Cardinality constraints (required and prohibited elements)
- Fixed value constraints (Code and Uri data types)
- Pattern value constraints (CodeableConcept and Identifier data types)
- Reference type constraints (FHIRPath resolve/is/conformsTo functions)
- Extension constraints (FHIRPath
conformsTofunction) - Vocabulary constraints (FHIRPath
memberOffunction) - Choice type constraints (FHIRPath
asfunction)
NOTE: there is currently no support for closed or ordered slices.
For example, the HL7 bodyweight profile has the following cardinality and fixed value constraints (some details removed for brevity):
{"id": "Observation.code.coding:BodyWeightCode.system","path": "Observation.code.coding.system","min": 1,"max": "1","type": [{"code": "uri"}],"fixedUri": "http://loinc.org"
{"id": "Observation.code.coding:BodyWeightCode.code","path": "Observation.code.coding.code","min": 1,"max": "1","type": [{"code": "code"}],"fixedCode": "29463-7",
which are used by the ConstraintGenerator to generate the following FHIRPath expression:
code.where(coding.where(system = 'http://loinc.org' and code = '29463-7').exists()).exists()
The HL7 bodyweight profile has the following reference type constraint (some details removed for brevity):
{"id": "Observation.subject","path": "Observation.subject","type": [{"code": "Reference","targetProfile": ["http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/Patient"]}]
which is used by the ConstraintGenerator to generate the following FHIRPath expression:
subject.resolve().is(Patient)
Complex reference types are also supported, for example:
derivedFrom.exists() implies (derivedFrom.all(resolve().is(DocumentReference) or resolve().is(ImagingStudy) or resolve().is(Media) or resolve().is(QuestionnaireResponse) or resolve().is(MolecularSequence) or resolve().conformsTo('http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/vitalsigns')))
is generated from the element definition Observation.derivedFrom in the same bodyweight profile.
FHIRPath based constraints specified in StructureDefinition.snapshot.element.constraint elements, will also be evaluated during profile validation. All of the constraints generated for a given profile are cached in memory so that they can be reused to validate multiple resources that are asserting conformance to the same profile.
Making profiles available to the FHIR registry component (FHIRRegistry)
The FHIR registry component keeps track of definitional resource types (e.g. StructureDefinition, ValueSet, CodeSystem, etc.). It uses the Java ServiceLoader to look for implementations of the FHIRRegistryResourceProvider interface:
public interface FHIRRegistryResourceProvider {/*** Get the registry resource from this provider for the given resource type, url and version** <p>If the version is null, then the latest version of the registry resource is returned (if available)** @param resourceType* the resource type of the registry resource* @param url
Package your implementation in a jar file and be sure to include its fully-qualified classname in your jar’s
META-INF/services/org.linuxforhealth.fhir.registry.spi.FHIRRegistryResourceProvider, then drop this jar in the server’s userlib directory to make it available to the server during startup.
NPM package format support
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server Registry module (fhir-registry) has utilities that can be used to expose FHIR registry resources that exist in the NPM package format. Implementation guides that follow this packaging format can be dropped into the src/main/resources/ under a directory structure defined by the ImplementationGuide.packageId value. For example, US Core implementation guide has a package id of: hl7.fhir.us.core. The NPM “package” folder can be dropped here: src/main/resources/hl7/fhir/us/core/package
For convenience, we have created a base implementation of FHIRRegistryResourceProvider called PackageRegistryResourceProvider. The implementation of the USCoreResourceProvider using this implementation looks like this:
public class USCoreResourceProvider extends PackageRegistryResourceProvider {@Overridepublic String getPackageId() {return "hl7.fhir.us.core";}}
The PackgageRegistryResourceProvider class converts the packageId (e.g. hl7.fhir.us.core) to a path where it can find the NPM package index file: .index.json. The PackageRegistryResourceProvider class creates FHIRRegistryResource instances, using the index file, and caches them in a map on startup. The PackageRegistryResource (an implementation of FHIRRegistryResource class lazily loads the underlying FHIR resource into memory when it is accessed. Multiple versions of the same resource can be registered. FHIR registry resource providers can be bundled into a jar file and deployed with the LinuxForHealth FHIR Server in the user lib directory.
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server uses the Snapshot and not the Differential, you must include a Snapshot. As mentioned in #2829, you may use FHIR Sushi with the -s option to generate a Snapshot.
For more information, please see: https://confluence.hl7.org/display/FHIR/NPM+Package+Specification
Built-in profile support
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server has built-in support for the following:
- Profiles defined in the base FHIR Specification (v4.0.1: R4 - Mixed Normative and STU) http://hl7.org/fhir/profilelist.html
Optional profile support
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server project includes modules for select FHIR implementation guides and makes versions of those available in both Maven Central and in the fhir-validation-distribution.zip artifact, which may be downloaded from https://github.com/LinuxForHealth/FHIR/releases. To make an implemenation guide available to the server, copy the corresponding jar (e.g. fhir-ig-us-core-VERSION.jar) to the LinuxForHealth FHIR Server’s userlib directory before startup.
In many cases, these modules wrap multiple versions of the corresponding implementation guide. By default, the server will use the latest version of given resource for validation purposes. See Section 4.5.3 of the User’s Guide for related configuration options.
Below is the list of implementation guides that are packaged as part of the project and which implementation guide versions they include:
| Implementation Guide | Packaged Versions |
|---|---|
| US Core | 3.1.1, 4.0.0, 5.0.1 |
| CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for BlueButton®) | 1.0.0, 1.1.0 |
| minimal Common Oncology Data Elements (mCODE) | 1.0.0 |
| Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HREX) | 1.0.0 |
| Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange (PDEX) | 1.0.0, 2.0.0 |
| Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange (PDEX) Plan Net | 1.0.0, 1.1.0 |
| Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange (PDex) US Drug Formulary | 1.0.1, 1.1.0 |
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server $validate operation
The LinuxForHealth FHIR Server provides a basic implementation of the $validate operation that invokes the FHIRValidator via a REST API. By default, the $validate operation will validate a resource against the base specification and any profiles asserted in its Resource.meta.profile element. The default behavior may be changed in one of the following ways:
- If a profile is specified via the optional
profileparameter, the $validate operation will validate a resource against the base specification and the specified profile only. It will not validate against any profiles asserted in theResource.meta.profileelement. - If the
profileparameter is not specified, but themodeparameter is specified, and themodeparameter value is eithercreateorupdate, the $validate operation will validate a resource against the base specification and any profiles asserted in itsResource.meta.profileelement, but will do so based on profile configuration properties specified in thefhirServer/resources/<resourceType>/profilessection of thefhir-server-config.jsonfile (see the user guide for configuration details).
ValueSet membership checking (FHIRPath memberOf function)
Coded elements (code, Coding, CodeableConcept data types), maybe have a binding element that specifies a ValueSet that that element is bound to. This means that the coded element must have a value that comes from that value set. The FHIR profile component will expand value sets according to the ValueSet expansion algorithm for ValueSets that include CodeSystem resources available via the FHIR registry component.
fhir-path-cli - command line execution of fhirpath over a FHIR Resource
The fhir-path-cli enables commandline processing of a FHIR Path over a FHIR resource and outputs the results.
For details on the fhir-path-cli, refer to the README.md